~~
This article contains 3 problems which have the similar topic but the difficulties are step-up one by one.
这篇文章包含了3个问题,都是关于数组查重,但难度是递进的
~~
Description 1
Given an array of integers, find if the array contains any duplicates.
Your function should return true if any value appears at least twice in the array, and it should return false if every element is distinct.
Example 1:
Input: [1,2,3,1]
Output: true
Example 2:
Input: [1,2,3,4]
Output: false
Example 3:
Input: [1,1,1,3,3,4,3,2,4,2]
Output: true
Analysis
判断数组内是否有重复元素,比较简单。两个思路,一个是用HashTable,另一个是先sort再compare
Solution
Approach #1 (HashTable)
public boolean containsDuplicate(int[] nums) {
HashSet
---
> **接下来,问题稍微升级一下**
>
> **Let's make the problem more complex**
---
## Description 2
Given an array of integers and an integer k, find out whether there are two distinct indices i and j in the array such that nums[i] = nums[j] and the absolute difference between i and j is at most k.
Example 1:
Input: [1,2,3,1], k = 3 Output: true
Example 2:
Input: [1,0,1,1], k = 1 Output: true
Example 3:
Input: [1,2,1], k = 0 Output: false
## Analysis
依旧是判断数组内是否有重复元素,不同的是加了一个长度限制k,所以我们要找的是在k长度内是否存在重复元素。
我自己的做法是用HashMap, key记录元素值,value记录位置,当发现重复元素且位置差不超过k时返回true。
另一个思路是使用HashSet,比如说,对于nums = {1,2,3,1}, k = 2来说,第一个1出现在位置0,当遍历到位置2还不是1的时候,就说明之后也不可能有值能符合条件了,所以我们就把第一个1删掉,只考虑{2,3,1},之后以此类推,具体的做法就是使HashSet的长度保持不大于k,一旦超过,就删掉最开头的元素。
## Approach
### Approach #1 (HashMap)
public boolean containsNearbyDuplicate(int[] nums, int k) { HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { Integer temp = map.put(nums[i],i); if (temp != null && i-temp <= k) { return true; } } return false; }
#### Complexity analysis
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(n)
### Approach #2 (HashSet)
public boolean containsNearbyDuplicate(int[] nums, int k) {
HashSet
#### Complexity analysis
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(min(n,k))
---
> **继续升级问题**
>
> **make it more complex**
---
## Description 3
Given an array of integers, find out whether there are two distinct indices i and j in the array such that the absolute difference between nums[i] and nums[j] is at most t and the absolute difference between i and j is at most k.
Example 1:
Input: [1,2,3,1], k = 4, t = 0 Output: true
Example 2:
Input: [1,0,1,1], k = 1, t = 0 Output: true
Example 3:
Input: [4,2], k = 2, t = 1 Output: false
## Analysis
在D2多了一个长度k的基础上,这次条件又多了一个t,意思是说如果两个元素的差不超过t的话,我们就把这两个元素近似看成是duplicate。
我自己做的时候是用`HashSet`,在问题2保持`HashSet`长度不超过k的基础上,每遍历到一个新值,就把该值与`HashSet`中的值逐一求差,当发现差不超过t时就返回true。当然,这样做的复杂度是`O(n*min(n,k))`,每次迭代都要遍历一遍`HashSet`。
一个比较好的思路是使用Buckets。有种排序方法叫bucket sort,也就是所谓的桶排序。结合下面这个图,可以看出桶排序的思路:把所有的数分到多个bucket中,然后对每个bucket里的数分别排序,然后再合起来。怎么分呢?给一个range,比如下图的range是10,也就是把所有的数按每10个一分,每个bucket有一个label,label = x/10,label相同的数就表示在一个桶里。
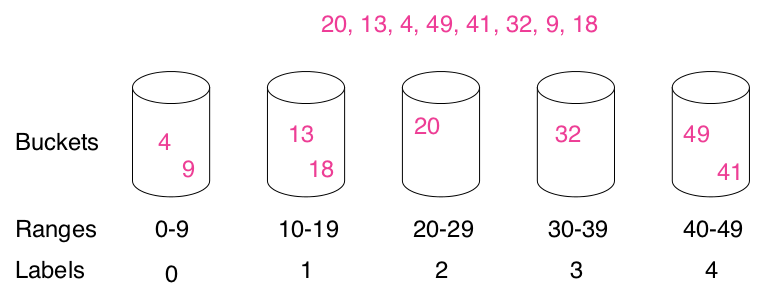
题目里给了t,表示在只要两个数的差不超过t就把这两个数看成是相同的,那么我们可以把每个bucket的range设成是t,那么只要是在同一个桶里有两个值,就可以返回true了。如果两个数不在同一个bucket,会不会也符合条件呢?有可能,这里还要考虑相邻的bucket。也就是说,一共要考虑两种情况:两个值在同一个bucket里,返回true;两个值在相邻的bucket,就计算他们的差是否超过t,如果不超过,返回true。用这个方法,复杂度是O(n),因为每次迭代里是O(1)的操作。
另外,这个题还要考虑Integer的范围问题,两个Integer的差有可能超过Integer的最大值,所以要用到long类型。
## Approach
### Approach #1 (Linear Search)
public boolean containsNearbyAlmostDuplicate(int[] nums, int k, int t) {
HashSet
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (i > k) set.remove(nums[i-k-1]);
for (int s : set) {
if (Math.abs((long)nums[i]-(long)s) <= (long)t) return true;
}
set.add(nums[i]);
}
return false; } ```
Complexity analysis
- Time complexity: O(n*min(n,k))
- Space complexity: O(min(n,k)). depends on the size of HashSet
Approach #2 (Buckets)
class Solution {
public long getBucketId(long x, long w) {
// here need to consider x is positive and negative
return (x < 0) ? (x+1)/w-1 : x/w;
}
public boolean containsNearbyAlmostDuplicate(int[] nums, int k, int t) {
if (t < 0) return false;
HashMap<Long, Long> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
long w = (long)t + 1;
if (i > k) map.remove(getBucketId(nums[i-k-1], w));
long id = getBucketId(nums[i], w);
if (map.containsKey(id)) return true;
if (map.containsKey(id-1) && (long)nums[i] - map.get(id-1) <= (long)t) return true;
if (map.containsKey(id+1) && map.get(id+1) - (long)nums[i] <= (long)t) return true;
map.put(id, (long)nums[i]);
}
return false;
}
}
Complexity analysis
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(min(n,k)). depends on the size of HashMap
There is another method using Binary Search Tree, which is to be continued..

Comments powered by Talkyard.